JSON
- ’{}’로 시작하며 Key Value쌍으로 데이터를 작성한다.
- 지원 Type
- String : value
- number : value
- boolean : value
- object : value { }
- array : value [ ]
- JSON에서는 snakecase를 더 많이 사용한다. → 하지만 두 가지 다 파싱 및 제공이 가능해야한다.
- ex
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
{
"phone_number" : "010-4459-4995",
"age" : 10,
"isAgree" : false,
"account" : {
"email" : "kmslkh@naver.com",
"password" : "1234"
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
//user 조회
{
"user_list" : [
{
"account" : "abcd",
"password" : "1234"
},
{
"account" : "bbbb",
"password" : "1234"
},
]
}
POST
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
package com.example.post.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class PostApiController {
@PostMapping("/post")
public void post(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> requestData){
requestData.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("key : " + key);
System.out.println("value : " + value);
});
}
@PostMapping("post1")
public void post1(@RequestBody PostRequestDto postRequestDto){
System.out.println(postRequestDto.toString());
}
}
- RequestBody Annotation을 사용한다.
- DTO의 경우 각 멤버 변수 명이 JSON Key와 같아야하는데 JAVA에서는 camelCase로 작성되는데 JSON에서는 snake_case로 전송될 수 있다.
- 다양한 해결 방법이 존재 한다.
JsonProperty로 다른 Case를 매칭 시킬 수 있다.
1 2
@JsonProperty("phone_number") private String phoneNumber;
PUT
- POST와 거의 유사하다.
CarDto
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
public class CarDto {
private String name;
@JsonProperty("car_number")
private String carNumber;
}
PutRequestDto
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
...
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.PropertyNamingStrategy;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonNaming;
...
@JsonNaming(value = PropertyNamingStrategy.SnakeCaseStrategy.class)
@Setter
@Getter
@ToString
public class PutRequestDto {
private String name;
private int age;
private List<CarDto> carList;
}
PutApiController
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
package com.example.put.controller;
import com.example.put.dto.PutRequestDto;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PutMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class PutApiController {
@PutMapping("/put")
public PutRequestDto put(@RequestBody PutRequestDto putRequestDto){
System.out.println(putRequestDto.toString());
return putRequestDto;
}
}
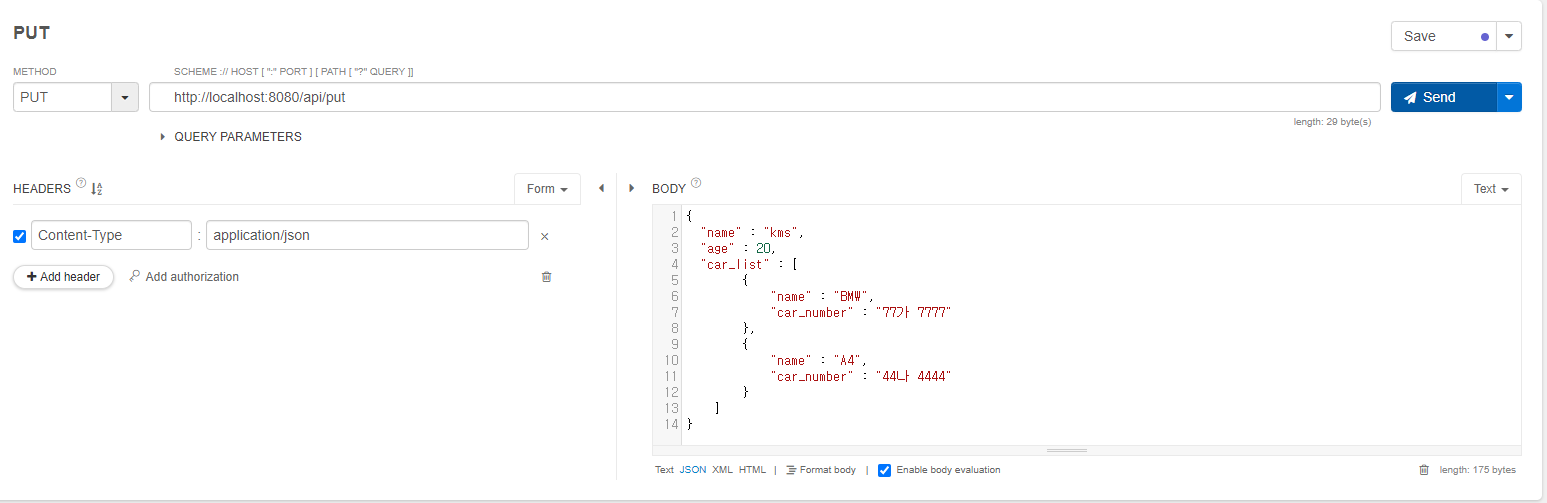
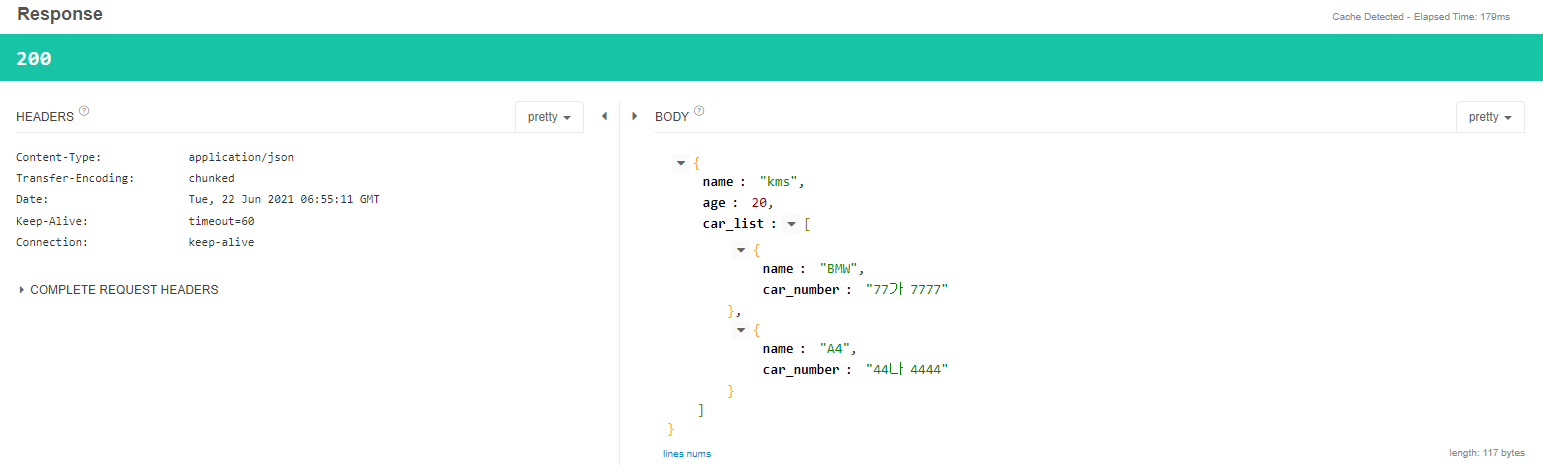

- camelCase, snake_case의 mapping은 JsonProperty를 사용해 변수별로 지정할 수 도 있고, JsonNaming을 사용해 Class단위로 지정할 수 도 있다.
- Sprint Boot RestController에서는 object를 return할 때 설정 한 JsonNaming, JsonProperty의 룰에 따라 JSON으로 변경되어 Response가 전송된다.